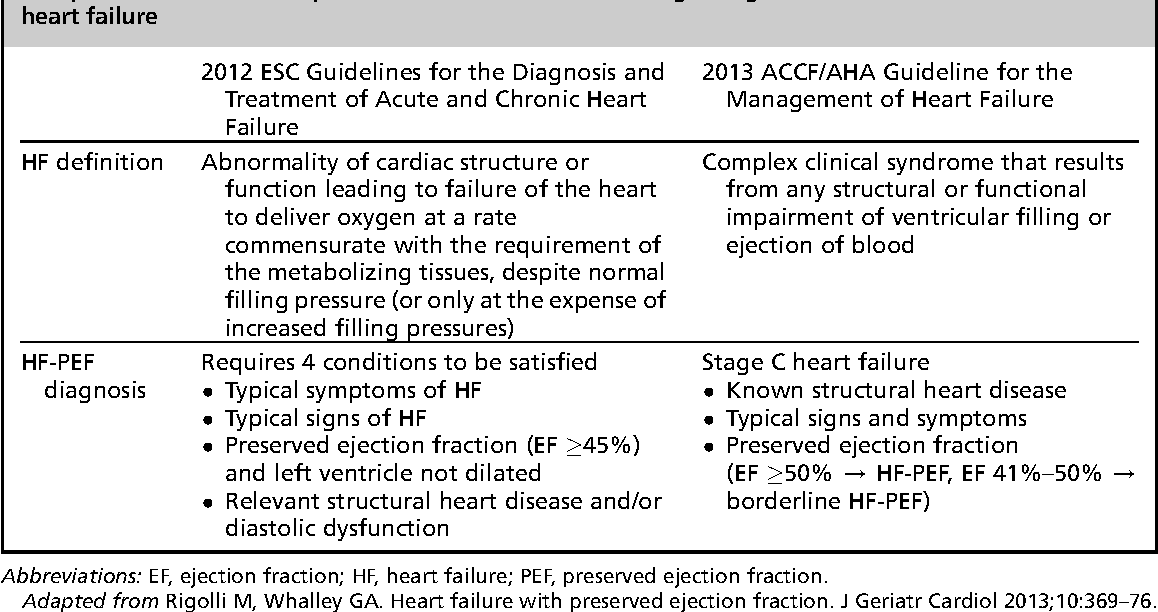
Structural Heart Disease Definition
Structural heart disease definition. Structural heart disease is a defect or abnormality of the heart that is non-coronary meaning that it does not affect the blood vessels in the heart. Many structural heart diseases are congenital con-JEN-it-al which means present at birth. Structural heart disease is a problem with the tissues or valves of the heart.
What is Structural Heart Disease. That is it occurs during the formation of the heart as a fetus develops. Presence of structural heart disease especially LV systolicdysfunction.
Structural heart disease cardiac dysfunction and heart failure. Structural heart disease also known as structural cardiac disease is a collection of heart diseases that includes heart failure coronary artery disease hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and congenital heart disease. Common structural heart disease conditions include but arent limited to.
Some structural heart disease will develop later in life. Rheumatic heart disease and all of its different valvular abnormalities including mitral. Structural heart disease refers to heart disease that is acquired through wear and tear or heart disease that people are born with.
Structural heart disease is any abnormality or defect of the heart muscle or the heart valves. Structural heart disease a term commonly used to describe defects or disorders in the hearts structureits valves for instance. An example of structural heart disease acquired through wear and tear would be a tight or leaky heart valve.
Most people with hypertension or diabetes will develop structural heart disease which might cause renal water and salt retention and eventually symptoms and. These defects can include. This is different from coronary artery disease which concerns the hearts plumbing or problems with the blood vessels that feed the heart such as narrowed or blocked arteries that can lead to heart attack.
In other words its a non-coronary disease that is caused by a structural defect rather than an artery or vein issue. Structural heart diseaserefers to a defect or abnormality in the hearts valves heart muscle or blood vesselsthat can be present at birth congenital or acquired later in life.
Many structural heart conditions are congenital present at birth but these abnormalities can also form later in life due to wear and tear from aging infection or result from another.
You may have heard of congenital heart disease. Definitions of structural heart disease are arbitrary. You may have heard of congenital heart disease. Structural heart disease is a problem with the tissues or valves of the heart. These defects can include. An example of structural heart disease acquired through wear and tear would be a tight or leaky heart valve. Structural heart disease a term commonly used to describe defects or disorders in the hearts structureits valves for instance. An example of structural heart disease people are born with would be a hole within the chambers of the heart. What Is Structural Heart Disease.
Structural heart disease is a defect or abnormality of the heart that is non-coronary meaning that it does not affect the blood vessels in the heart. Structural heart disease is a defect or abnormality of the heart that is non-coronary meaning that it does not affect the blood vessels in the heart. Events leading to heart disease progression - Text Description. Structural heart disease is an umbrella term for a number of defects which affect the valves and chambers of the heart and the aorta. Structural heart disease cardiac dysfunction and heart failure. Structural heart disease is a general term used to describe conditions that involve damage to or flaws in the anatomy of the heart. An example of structural heart disease acquired through wear and tear would be a tight or leaky heart valve.

































Post a Comment for "Structural Heart Disease Definition"