Enteroaggregative E. Coli Treatment
Enteroaggregative e. coli treatment. Coli VTEC or enterohemorrhagic E. Coli EAEC require different detection methods since they do not produce Shiga toxin. Studies have suggested that fluoroquinolone especially ciprofloxacin may be the most effective antibiotic when treating Enteroaggregative Ecoli EAEC infections patients treated with ciprofloxacin had significant reductions in duration of diarrhea.
Coli EPEC Enteroaggregative E. The availability of suitable diagnostic tests for enterohaemorrhagic E coli EHEC typified by E coli O157 another emergent category of diarrhoeagenic E coli has been instrumental in the prevention and correct management of infected cases identification of cattle as principal reservoirs detection of the pathogen in food and improvement of food processing and handling. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli EAEC Strain in a Novel Weaned Mouse Model.
Effects of enteroaggregative E. Coli EAEC induces diarrhoeal illness although it is typically less severe than that caused by EHEC and EPEC. The pur-pose of this article is to provide health care workers with an update on the epidemiology clinical mani-festations diagnostic modalities and treatment of EAEC infection.
Coli EPEC enteroinvasive E. Although infection responds to antibiotic therapy increasing antibiotic resistance and the widespread nature of the infection limit the utility of antibiotics. The toxins and the diseases that ETEC causes are not related to E.
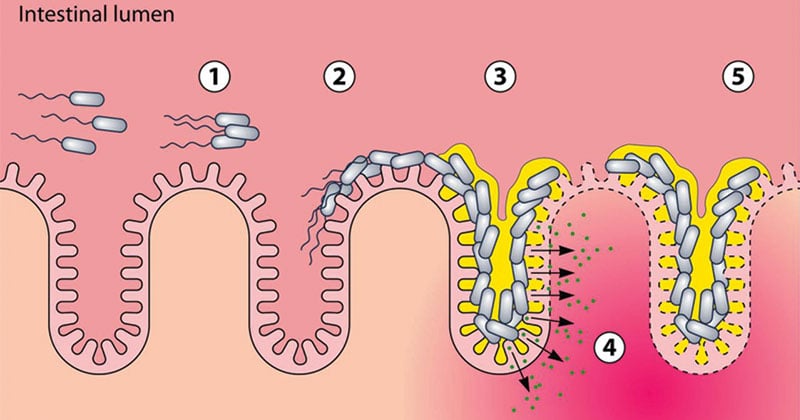
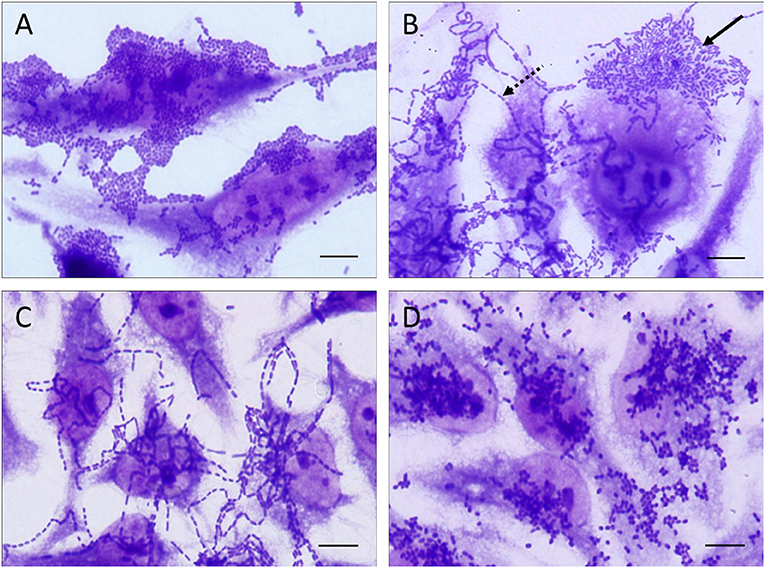
Transmission electron microscopy reveals adherence of bacteria to the apical surface of the T84 cells without internalization. Coli ETEC enteropathogenic E. Coli that produce special toxins which stimulate the lining of the intestines causing them to secrete excessive fluid thus producing diarrhea.
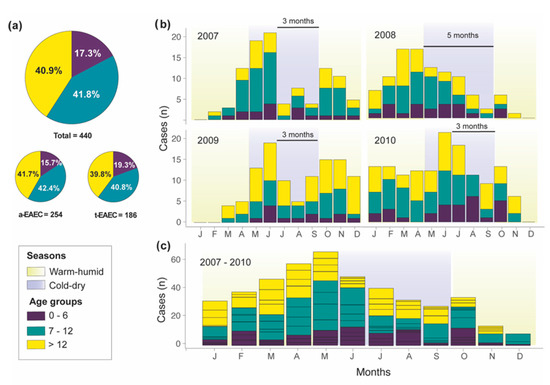
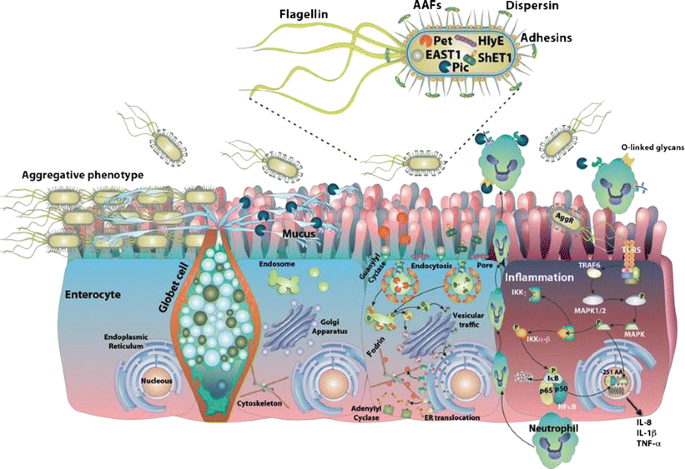
Exacerbation by Malnutrition Biofilm as a Virulence Factor and Treatment by Nitazoxanide Background Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli EAEC is increasingly recognized as a common cause of diarrhea in healthy malnourished and immune-deficient adults and children. Coli strains STEC can be detected through targeting Shiga toxins via molecular or immunoassays. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli EAEC is an emerging diarrheal pathogen implicated in travelers diarrhea and endemic diarrhea in developing and industrialized countries.
Coli EIEC and enteroaggregative E. Publication types Research Support US.
Exacerbation by Malnutrition Biofilm as a Virulence Factor and Treatment by Nitazoxanide Background Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli EAEC is increasingly recognized as a common cause of diarrhea in healthy malnourished and immune-deficient adults and children.
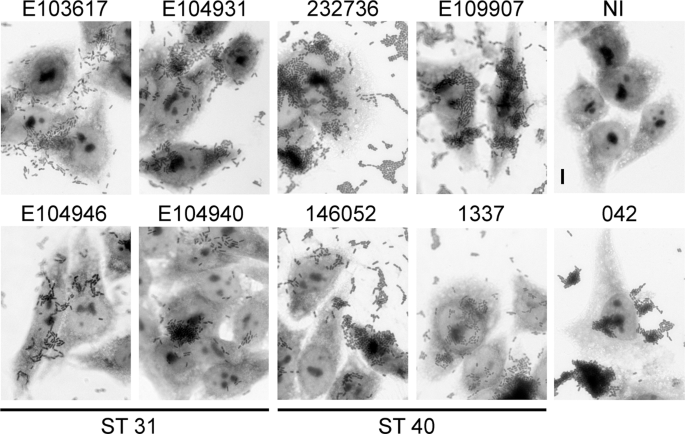
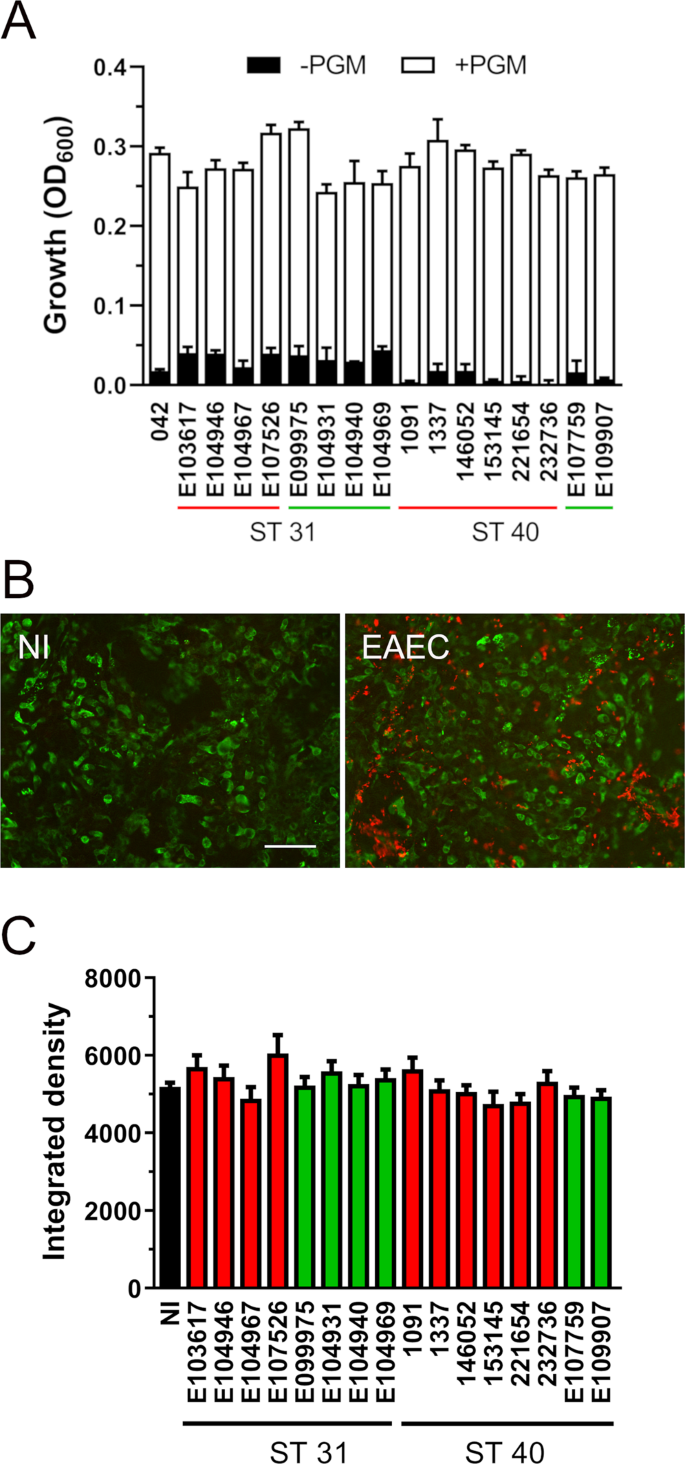
Transmission electron microscopy reveals adherence of bacteria to the apical surface of the T84 cells without internalization. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli EAEC was first described in 1987 in a child with acute diarrhea in Lima Peru and has since been linked with persistent diarrhea in children living in areas where EAEC is endemic individuals with human immunodeficiency virus infection and as a cause of diarrhea in travelers from industrialized countries visiting less-developed areas of the world. Coli ETEC enteropathogenic E. Coli VTEC or enterohemorrhagic E. Enteroaggregative Escherichia coli EAEC Strain in a Novel Weaned Mouse Model. Publication types Research Support US. This pathotype is the one most commonly heard about in the news in association with foodborne outbreaks. Polarized T84 monolayers were washed and inoculated with 10 6 CFU of 042 and allowed to coincubate at 37C for 6 hrs. Other diarrheagenic strains enterotoxigenic E.
Coli ETEC enteropathogenic E. Coli EPEC Enteroaggregative E. Although infection responds to antibiotic therapy increasing antibiotic resistance and the widespread nature of the infection limit the utility of antibiotics. Polarized T84 monolayers were washed and inoculated with 10 6 CFU of 042 and allowed to coincubate at 37C for 6 hrs. The availability of suitable diagnostic tests for enterohaemorrhagic E coli EHEC typified by E coli O157 another emergent category of diarrhoeagenic E coli has been instrumental in the prevention and correct management of infected cases identification of cattle as principal reservoirs detection of the pathogen in food and improvement of food processing and handling. Understanding of EAEC pathogenesis is rapidly increasing and advances are proving relevant to epidemiologic and clinical investigations. Coli EPEC enteroinvasive E.























Post a Comment for "Enteroaggregative E. Coli Treatment"